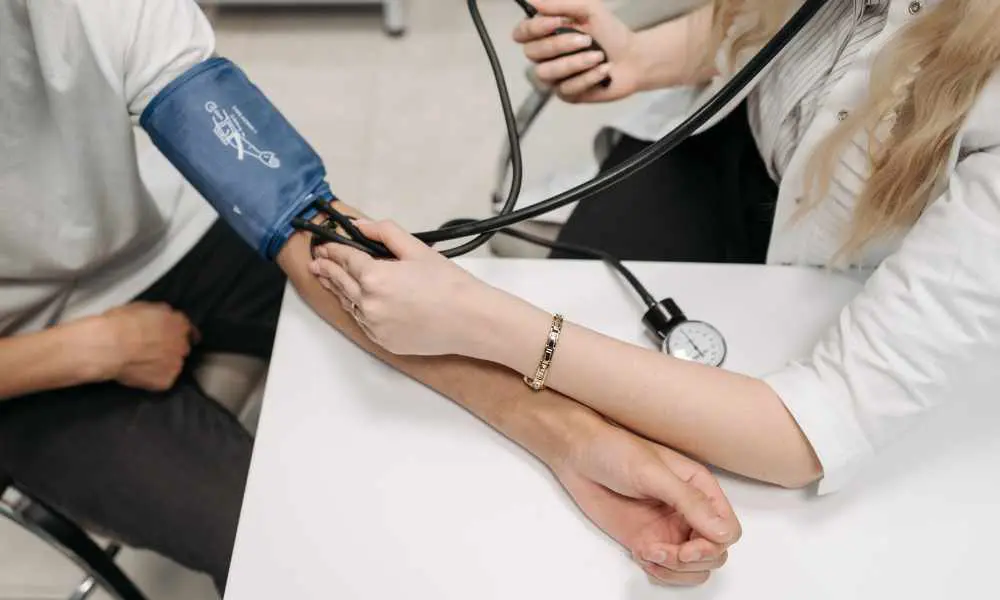
In the realm of healthcare, precision and accuracy are paramount, especially when it comes to monitoring vital signs. One such indispensable tool in a medical professional’s arsenal is the Aneroid Sphygmomanometer. This article delves into the significance of Aneroid Sphygmomanometers, exploring their history, functionality, and the pivotal role they play in measuring blood pressure accurately.
The Evolution of Aneroid Sphygmomanometers:
Origins and Development:
The Aneroid Sphygmomanometer traces its roots back to the 19th century when the need for non-invasive blood pressure measurement became apparent. Invented by Samuel Siegfried Karl Ritter von Basch in 1881 and further refined by Scipione Riva-Rocci in 1896, the device underwent continuous improvements.
Advancements in Design:
Over the years, advancements in technology and materials have contributed to the evolution of Aneroid Sphygmomanometers. Modern designs feature durable, lightweight materials such as aluminum, making them portable and easy to use in various healthcare settings.
The Role of Aneroid Sphygmomanometers in Preventive Medicine:
Early Detection of Hypertension:
Aneroid Sphygmomanometers play a pivotal role in preventive medicine by facilitating the early detection of hypertension. Regular blood pressure monitoring helps identify individuals with high blood pressure, enabling timely intervention and lifestyle modifications. The simplicity and accessibility of Aneroid Sphygmomanometers make them essential tools in community health screenings and primary care settings, contributing to the prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
Patient Empowerment through Self-Monitoring:
Empowering patients to actively participate in their healthcare is a growing trend, and Aneroid Sphygmomanometers support this shift. Many individuals with chronic conditions, such as hypertension, are encouraged to monitor their blood pressure at home. Aneroid Sphygmomanometers, with their user-friendly design, enable patients to regularly measure their blood pressure, fostering a sense of control and awareness regarding their health status.
How Aneroid Sphygmomanometers Work:
Basic Components:
An Aneroid Sphygmomanometer comprises a few essential components, including an inflatable cuff, a pressure bulb, a pressure control valve, and a gauge. The gauge is a crucial element, as it displays the pressure readings accurately.
Inflation and Deflation:
During a blood pressure measurement, the cuff is inflated to a pressure higher than the systolic blood pressure. The pressure is then gradually released, allowing healthcare professionals to detect the systolic and diastolic blood pressure values based on the sounds produced by blood flow through the arteries.
Accuracy and Calibration:
Calibration Process:
Ensuring the accuracy of Aneroid Sphygmomanometers is crucial for reliable blood pressure readings. Regular calibration is necessary to maintain precision. Healthcare professionals often use a mercury manometer, considered the gold standard for accuracy, to calibrate Aneroid Sphygmomanometers.
Importance of Accuracy:
Inaccurate blood pressure readings can lead to misdiagnosis and improper treatment, emphasizing the critical role of calibrated Aneroid Sphygmomanometers in healthcare. The device’s reliability is vital in managing conditions such as hypertension, where precise measurements guide treatment decisions.
Benefits and Applications:
Portability and Convenience:
One of the primary advantages of Aneroid Sphygmomanometers is their portability. Medical professionals can easily carry these devices, making them ideal for home visits, ambulatory care, and emergency situations. Their convenience extends the reach of blood pressure monitoring beyond traditional clinical settings.
Cost-Effectiveness:
Compared to automated or electronic blood pressure monitors, Aneroid Sphygmomanometers are more cost-effective. This affordability allows healthcare facilities, especially those in resource-limited settings, to equip themselves with essential monitoring tools without compromising accuracy.
Challenges and Maintenance:
Vulnerability to Damage:
Despite their benefits, Aneroid Sphygmomanometers are susceptible to damage, particularly from drops or mishandling. Accurate readings hinge on the device’s integrity, emphasizing the need for careful maintenance.
Regular Inspection:
Healthcare professionals must routinely inspect Aneroid Sphygmomanometers for any signs of wear, tear, or calibration issues. Regular checks and prompt repairs or replacements ensure that the device continues to provide accurate blood pressure measurements.
Conclusion:
In the realm of healthcare, the Aneroid Sphygmomanometer stands as a testament to the fusion of historical innovation and modern technology. Its portable design, cost-effectiveness, and accuracy make it an invaluable tool for monitoring blood pressure in diverse healthcare settings. As medical science continues to evolve, the Aneroid Sphygmomanometer remains a stalwart companion for healthcare professionals, enabling them to make informed decisions and provide optimal care to their patients.